This is an old revision of the document!
The following is my understanding and interpretation of the proposal from Michael S. Tsirkin. https://lists.gnu.org/archive/html/qemu-devel/2015-08/msg03993.html
Jun Nakajima
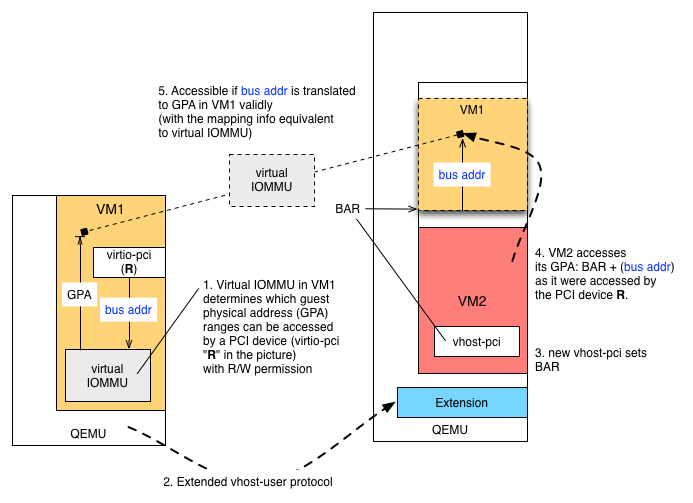
VM1, VM2 corresponding to the examples in his proposal. Basically VM1 can express access permission (R/W) to its guest physical address (GPA) space by virtual IOMMU. Typically, IOMMU (e.g. AMD-Vi and Intel VT-d) uses page tables that convert bus (I/O) address to GPA for a given PCI device to protect the rest of the system from the DMA operations. See https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/vfio.txt for the details and VFIO.
If you think about an imaginary (i.e. virtual) PCI device "R", you can set up mapping from bus (I/O) address to GPA for that device (because you can set up such mapping for each PCI device). This way, VM1 "gets full control of its security, from mapping all memory (like with current vhost-user) to only mapping buffers used for networking (like ivshmem) to transient mappings for the duration of data transfer only."
General DMA Operations and Protection
If the device driver of R sets up a buffer to receive data, programming the registers, data will be put into the buffer as DMA. Then the device R generates an interrupt (maybe putting more data to other buffers). The IOMMU makes sure that data (addressed by bus or I/O address) be translated to GPA. If the mapping is not valid, then IOMMU reports an error (via MSI). This way, VM1 is protected against the DMA operations made by the device R. Once the DMA operation is done, the IOMMU transaction is done.
Inter-VM Communication
How can this mechanism is used for inter-VM communication? It should be easy. In this example, VM1 receives data from VM2. For example, DPDK runs on VM2, forwarding packets to VM1.
One of the simplest ways would be (Rx for VM1):
- In VM1 the device driver uses polling to keep DMA operations of R open
- For performance reasons, the buffer addresses should be static or covered by larger regions that are mapped by virtual IOMMU. The mapping is determined and established by VM1.
- A process or kernel in VM2 accesses BAR + (bus address) in its GPA to copy data to VM1